smorgasbord
Well-Known Member
- Region
- USA
We've got some scattered threads on chain cleaning, lubing, and measuring, but my hope here is to unite the best thinking and experiences from our community into one thread. If you've got some good tips or techniques to share, go right ahead.
Cleaning:
I did the first deep clean of my newish bike's chain today (about 250 miles). I have an old Park Tool "Cyclone" unit that I used on my analog bike for many years. Without thinking I clamped it onto my chain and then, before filling with cleaning fluid, I realized that it wasn't going to work. That's because you have to run the chain backward, and as we mid-drive owners know, the mid-drive has a ratchet that doesn't let you do that (thankfully - otherwise the motor would be forcing our pedals around). So, I had to put the bike on a stand so the wheel could turn and mounted the Cyclone backward in order to be able to run the chain in the proper direction. Turns out the new Cyclone units can be assembled two ways to accommodate this, as discussed in Park Tool's directions.
I wasn't happy with how clean it got the chain, though, even after doing the second pass. And that's even ignoring the awkwardness of using the Cyclone. Then I remembered a bike mechanic years ago telling me that he just uses White Lightning's Clean Streak, which comes in an aerosol can. I had never really done that since it makes such a mess and the Cyclone was a pretty neat operation as far as chain cleaning goes, but I found plenty of other uses for Clean Streak (not just for cleaning, btw). Anyway, I put down a big sheet of cardboard, and with the red tube tip nozzle to concentrate the spray I sprayed the chain while slowly pedaling. Wow, that chain got clean fast. I used my air compressor to help dry it, then did another round with the Clean Streak, which I probably didn't need to do as the spray coming off the chain was almost perfectly clean, compared with the first pass. I dried the chain again with the compressor and a rag (directions say that wasn't necessary, FWIW).
I now swear by Clean Streak for chain cleaning, as long as you have a floor-coverable area in which you can spray (this is NOT for apartment dwellers!).
Chain Stretch:
The interwebs are filled with all sorts of folklore, criticisms of store-bought chain checking devices, and tips. It took me some time to understand what they are talking about when they say most of the standard checkers aren't accurate. I think I can explain it more simply, so here's my take:
A chain consists of plates connected by pins, with rollers surrounding the pins as the contact areas with the cogs. Here's an exploded diagram and photo:

Until I looked at the photo, I didn't understand the talk about "bushings." That's because bushings aren't really separate pieces. In the photo above they look like lips molded on the inside of the inside plates. The pins go inside the lips and the rollers go outside. There is no pin to roller contact (which is probably really important). The rollers are what ride on the cogs (rear cassette and front chainring).
So now, as the inside of the bushings and/or the outside of the pins wear, the chain gets longer because under tension the pins are now a bit further apart. This is bad because the roller locations won't line up with the cogs and will increase wear on those cogs. Here's a diagram (new chain at top):

You can see in the diagram above that the green bushings have worn "into" the red pins and this distance accumulates link by link. This is why the "old school" way of measuring a chain by measuring the distance between 24 pins works - 24 pins should be 12 inches. If it's 12&1/16" then you've had 0.5% wear and are at least 3/4 of the way towards needing to be replaced (Note: I've read 12-speed chains should be replaced at this point, not later). In terms of chain lengthening note that neither the inner nor the outer plates have actually changed length.
Let's look at other wear that happens. As the outside of the bushings and/or the inside of the rollers wear there's more play in the rollers, but the chain doesn't get longer. Here's a diagram showing this (new chain at the top):

As a result, bushing to roller play doesn't make the chain longer (as you can see the pins are the same distance apart), and this wear doesn't hurt the cogs because the cog will simply push the roller about the pin.
Commercial Chain Checkers:
The way most chain checkers work is that they're inserted between two rollers and push them apart. This measures not just the pin to bushing wear (chain lengthening), but also the bushing to roller wear (and play) of two pins. Here's a hypothetical chain with only roller/bushing wear being measured by a typical chain checker:

You can see that the pins are still the same distance apart, but the rollers are much further apart (vertical yellow lines for reference). This is due to them being pushed against the bushings from the inside. To add to that, even a new chain will measure some wear: do the mental push apart of the two outside rollers in the top (new) chain, and you'll see that you're also measuring the float of the rollers against the bushings as chain wear. I suspect this float is different for different chains.
Finally, note that the bushing to roller wear on the two inside links doesn't matter. Those rollers can float either way without affecting the length measurement. In other words, it's only two links from which bushing to roller wear is length-measurable, no matter how long a span you're measuring over. This looks really bad here because we're only measuring over 3 links (1.5"). If you were to measure over a foot (24 links), then the additional error from the two bushing/roller wears won't matter as much since you'll have pin to bushing wear from 24 links and only bushing to roller wear from two links. Unfortunately, most chain checkers don't measure more than 4"-5" and can't be much longer since they're designed to be used while the chain is on the bike.
Now, one way to avoid measuring bushing to roller wear would be to push the two rollers in the same direction. The theory being that bushing to roller wear is mostly the same on every pin, so if we push the two rollers the same way they'll both move by the same wear (and play) amount and thus cancel out that part of the wear. This is typically done by having 3 prongs on the checker tool: Length is measured from the center prong to the leftmost prong, while the rightmost prong pushes the chain against the center prong to get that center roller moved in the same direction as the leftmost prong is moving that roller.
Here's an older Shimano chain checker that works this way:
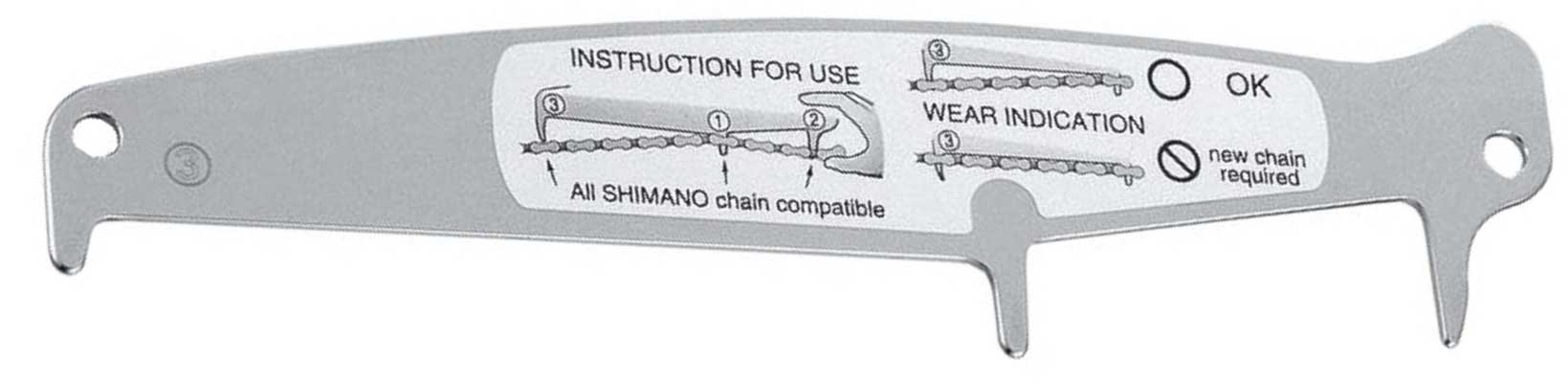
Notice the instructions say to put the center prong in first, then lightly squeeze the rightmost prong into the chain (this moves the roller to the left of the center prong), and only then do you measure with the leftmost prong.
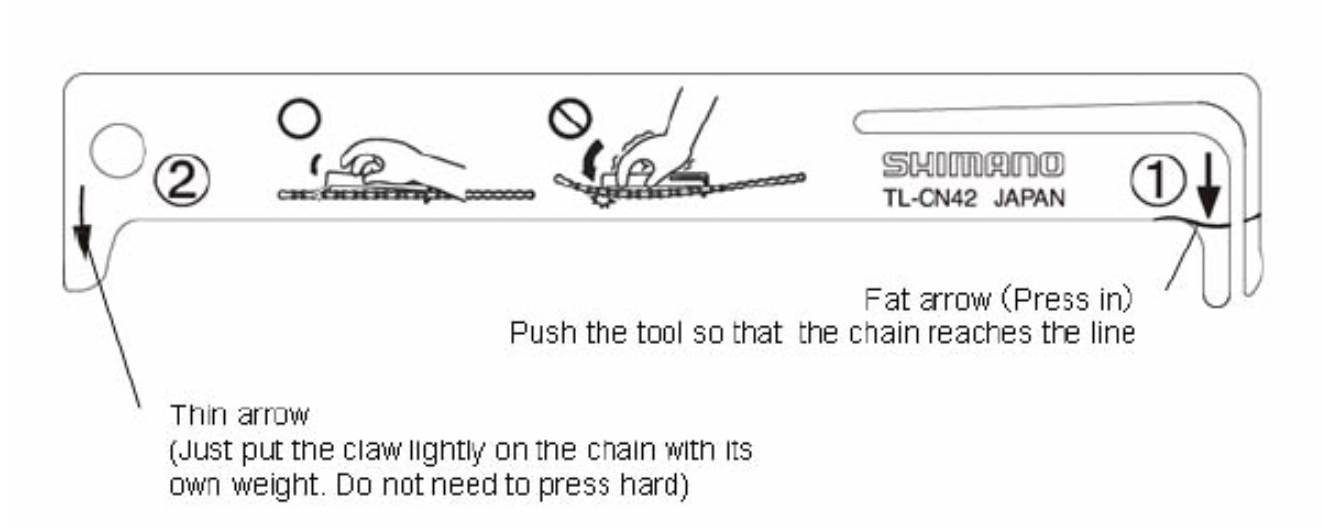
The new Park Tool CC-4 checker appears to be a copy of the Shimano (maybe it fell out of patent?). I own the newer Shimano TL-CN42, below, which I think is a bit better as the rightmost prong is actually kind of spring-loaded, so should require less skill to use:
Finally, note that SRAM Eagle chains use oversized rollers, and as a result, many common chain tools won’t even physically fit into the X01 and XX1-level SRAM chains (read here for details). I'm not sure what this means for the TL-CN42 checker that I own - it may be worthless for my bike, which uses a SRAM 12-speed chain. Hmmm.
Alternative Length Measurement Techniques:
Now, the old school measurement technique is to pull the chain off the bike and line it up against a ruler. This can work really well since you can measure over a foot or more and 1/16" over a foot isn't too hard to measure by eye. But, pulling the chain off the bike is a pain, even with snap-on master links.
There is at least one electronic measuring checker, but it has the same problems as the regular chain checkers since it pushes rollers apart instead of in the same direction.
Now the good stuff. I recently ran into a thread from 2010 on the mtbr.com forums that can be used with digital calipers to directly subtract the bushing to roller wear we don't want to measure. The way it works is that you:

Note on chain stretch tolerance with cheap drivetrains:
Eventually, a worn chain will break, as the pins are worn down they become thinner and then snap. Putting a new chain on then often means problems because the rear cassette cogs and front chainring have been worn by the elongated chain and no longer work well with a proper length chain. Replacing a chain at the 0.5%-0.75% thresholds will help your cassette and chainring last longer, which is why that's the recommendation. Those running expensive ($200 and up) SRAM or Shimano 11 or 12-speed cassettes should really pay attention. But, those people running cheap 7-speed systems where the cassette is really cheap (A Shimano Acera cassette is like $10-$18) might consider just letting the chain and cassette wear and then replace both at a lower per-mile cost (in $ and hassle). Not advice, but something to consider.
Chain Lube:
This will never be settled. The best any of us can do is provide anecdotal evidence, and how we ride (do we mash or spin, do we shift going uphill, do we ride in the rain or through mud) will always affect the results, not to mention that different chains will wear differently with the same lube. And of course, how the chain is maintained matters. Re-oiling a dirty chain can actually flush the smaller particles into the chain, which will accelerate wear.
I used Dumonde on my analog bike, and got great mileage (8K miles!) out of my Campy chain, but I almost never rode in the rain, was always on clean, paved roads, and don't shift going uphill. After reading this article, I've decided to use NFS on my 12-speed SRAM-equipped eBikes. It seems clear that the best chain lubricant is wax, either home-made or store-bought. Either way, wax is quite an involved procedure to apply.
Article Links:
Much of the above information was pulled from articles of varying completeness and accuracy. Here are the links if you want to do your own due-diligence or are just as OCD-interested as I was today:
Cleaning:
I did the first deep clean of my newish bike's chain today (about 250 miles). I have an old Park Tool "Cyclone" unit that I used on my analog bike for many years. Without thinking I clamped it onto my chain and then, before filling with cleaning fluid, I realized that it wasn't going to work. That's because you have to run the chain backward, and as we mid-drive owners know, the mid-drive has a ratchet that doesn't let you do that (thankfully - otherwise the motor would be forcing our pedals around). So, I had to put the bike on a stand so the wheel could turn and mounted the Cyclone backward in order to be able to run the chain in the proper direction. Turns out the new Cyclone units can be assembled two ways to accommodate this, as discussed in Park Tool's directions.
I wasn't happy with how clean it got the chain, though, even after doing the second pass. And that's even ignoring the awkwardness of using the Cyclone. Then I remembered a bike mechanic years ago telling me that he just uses White Lightning's Clean Streak, which comes in an aerosol can. I had never really done that since it makes such a mess and the Cyclone was a pretty neat operation as far as chain cleaning goes, but I found plenty of other uses for Clean Streak (not just for cleaning, btw). Anyway, I put down a big sheet of cardboard, and with the red tube tip nozzle to concentrate the spray I sprayed the chain while slowly pedaling. Wow, that chain got clean fast. I used my air compressor to help dry it, then did another round with the Clean Streak, which I probably didn't need to do as the spray coming off the chain was almost perfectly clean, compared with the first pass. I dried the chain again with the compressor and a rag (directions say that wasn't necessary, FWIW).
I now swear by Clean Streak for chain cleaning, as long as you have a floor-coverable area in which you can spray (this is NOT for apartment dwellers!).
Chain Stretch:
The interwebs are filled with all sorts of folklore, criticisms of store-bought chain checking devices, and tips. It took me some time to understand what they are talking about when they say most of the standard checkers aren't accurate. I think I can explain it more simply, so here's my take:
A chain consists of plates connected by pins, with rollers surrounding the pins as the contact areas with the cogs. Here's an exploded diagram and photo:
Until I looked at the photo, I didn't understand the talk about "bushings." That's because bushings aren't really separate pieces. In the photo above they look like lips molded on the inside of the inside plates. The pins go inside the lips and the rollers go outside. There is no pin to roller contact (which is probably really important). The rollers are what ride on the cogs (rear cassette and front chainring).
So now, as the inside of the bushings and/or the outside of the pins wear, the chain gets longer because under tension the pins are now a bit further apart. This is bad because the roller locations won't line up with the cogs and will increase wear on those cogs. Here's a diagram (new chain at top):
You can see in the diagram above that the green bushings have worn "into" the red pins and this distance accumulates link by link. This is why the "old school" way of measuring a chain by measuring the distance between 24 pins works - 24 pins should be 12 inches. If it's 12&1/16" then you've had 0.5% wear and are at least 3/4 of the way towards needing to be replaced (Note: I've read 12-speed chains should be replaced at this point, not later). In terms of chain lengthening note that neither the inner nor the outer plates have actually changed length.
Let's look at other wear that happens. As the outside of the bushings and/or the inside of the rollers wear there's more play in the rollers, but the chain doesn't get longer. Here's a diagram showing this (new chain at the top):
As a result, bushing to roller play doesn't make the chain longer (as you can see the pins are the same distance apart), and this wear doesn't hurt the cogs because the cog will simply push the roller about the pin.
Commercial Chain Checkers:
The way most chain checkers work is that they're inserted between two rollers and push them apart. This measures not just the pin to bushing wear (chain lengthening), but also the bushing to roller wear (and play) of two pins. Here's a hypothetical chain with only roller/bushing wear being measured by a typical chain checker:
You can see that the pins are still the same distance apart, but the rollers are much further apart (vertical yellow lines for reference). This is due to them being pushed against the bushings from the inside. To add to that, even a new chain will measure some wear: do the mental push apart of the two outside rollers in the top (new) chain, and you'll see that you're also measuring the float of the rollers against the bushings as chain wear. I suspect this float is different for different chains.
Finally, note that the bushing to roller wear on the two inside links doesn't matter. Those rollers can float either way without affecting the length measurement. In other words, it's only two links from which bushing to roller wear is length-measurable, no matter how long a span you're measuring over. This looks really bad here because we're only measuring over 3 links (1.5"). If you were to measure over a foot (24 links), then the additional error from the two bushing/roller wears won't matter as much since you'll have pin to bushing wear from 24 links and only bushing to roller wear from two links. Unfortunately, most chain checkers don't measure more than 4"-5" and can't be much longer since they're designed to be used while the chain is on the bike.
Now, one way to avoid measuring bushing to roller wear would be to push the two rollers in the same direction. The theory being that bushing to roller wear is mostly the same on every pin, so if we push the two rollers the same way they'll both move by the same wear (and play) amount and thus cancel out that part of the wear. This is typically done by having 3 prongs on the checker tool: Length is measured from the center prong to the leftmost prong, while the rightmost prong pushes the chain against the center prong to get that center roller moved in the same direction as the leftmost prong is moving that roller.
Here's an older Shimano chain checker that works this way:
Notice the instructions say to put the center prong in first, then lightly squeeze the rightmost prong into the chain (this moves the roller to the left of the center prong), and only then do you measure with the leftmost prong.
The new Park Tool CC-4 checker appears to be a copy of the Shimano (maybe it fell out of patent?). I own the newer Shimano TL-CN42, below, which I think is a bit better as the rightmost prong is actually kind of spring-loaded, so should require less skill to use:
Finally, note that SRAM Eagle chains use oversized rollers, and as a result, many common chain tools won’t even physically fit into the X01 and XX1-level SRAM chains (read here for details). I'm not sure what this means for the TL-CN42 checker that I own - it may be worthless for my bike, which uses a SRAM 12-speed chain. Hmmm.
Alternative Length Measurement Techniques:
Now, the old school measurement technique is to pull the chain off the bike and line it up against a ruler. This can work really well since you can measure over a foot or more and 1/16" over a foot isn't too hard to measure by eye. But, pulling the chain off the bike is a pain, even with snap-on master links.
There is at least one electronic measuring checker, but it has the same problems as the regular chain checkers since it pushes rollers apart instead of in the same direction.
Now the good stuff. I recently ran into a thread from 2010 on the mtbr.com forums that can be used with digital calipers to directly subtract the bushing to roller wear we don't want to measure. The way it works is that you:
- Measure the distance between two links (pushing apart). I recommend putting some pedal pressure (no motor!) into it to tighten the chain.
- Re-zero the calipers at that distance.
- Now measure the distance between 12 links, also pushing apart with pedal pressure on the chain. That's effectively measuring 10 links and should be exactly 5" with a new chain:
- If it measures 5.025" or less, you're under 0.5% of stretch. If you have a 12-speed chain, replace at 5.025", otherwise, you're 3/4 of the way to replacement.
- If it measures 5.038" or less, you're under 0.75% of stretch. Replace your chain at 5.038" (or just before).
- If it measures 5.050" or more, you're 1% or more stretched and likely have wear on your rear cassette and/or front chainring.
Note on chain stretch tolerance with cheap drivetrains:
Eventually, a worn chain will break, as the pins are worn down they become thinner and then snap. Putting a new chain on then often means problems because the rear cassette cogs and front chainring have been worn by the elongated chain and no longer work well with a proper length chain. Replacing a chain at the 0.5%-0.75% thresholds will help your cassette and chainring last longer, which is why that's the recommendation. Those running expensive ($200 and up) SRAM or Shimano 11 or 12-speed cassettes should really pay attention. But, those people running cheap 7-speed systems where the cassette is really cheap (A Shimano Acera cassette is like $10-$18) might consider just letting the chain and cassette wear and then replace both at a lower per-mile cost (in $ and hassle). Not advice, but something to consider.
Chain Lube:
This will never be settled. The best any of us can do is provide anecdotal evidence, and how we ride (do we mash or spin, do we shift going uphill, do we ride in the rain or through mud) will always affect the results, not to mention that different chains will wear differently with the same lube. And of course, how the chain is maintained matters. Re-oiling a dirty chain can actually flush the smaller particles into the chain, which will accelerate wear.
I used Dumonde on my analog bike, and got great mileage (8K miles!) out of my Campy chain, but I almost never rode in the rain, was always on clean, paved roads, and don't shift going uphill. After reading this article, I've decided to use NFS on my 12-speed SRAM-equipped eBikes. It seems clear that the best chain lubricant is wax, either home-made or store-bought. Either way, wax is quite an involved procedure to apply.
Article Links:
Much of the above information was pulled from articles of varying completeness and accuracy. Here are the links if you want to do your own due-diligence or are just as OCD-interested as I was today:
- The grand-daddy of chain wear articles, from which I colorized some hard to understand black and white diagrams for this post.
- A good article on chain wear from BikeRader.com.
- A posting with how to measure with vernier calipers, which I improved in the description above.
- A good general chain maintenance article.
- A good chain lube article.
- An older chain lube test report.
- EDIT: A very recent (Feb 2020) chain lube article that disagrees with the above chain lube test since it doesn't cover real-world short burst hard pedaling. This article references this 2018 lube test.
Attachments
Last edited:



